The artificial intelligence landscape has long been dominated by a few key players. Companies like OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic set the pace for innovation, building powerful AI models that required billions of dollars and massive computational resources. However, this dominance was recently challenged in an unexpected way. The emergence of DeepSeek R1, an open-source AI model, has disrupted the status quo, proving that cutting-edge AI can be developed efficiently and at a fraction of the cost. This breakthrough has sent shockwaves through the industry, forcing major tech companies to adapt and raising crucial questions about the future of AI leadership.
The AI Landscape Before DeepSeek
For years, OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic led the way, pushing the boundaries of what large language models (LLMs) could achieve. OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Gemini, and Anthropic’s Claude were considered the gold standard in AI capabilities, with high levels of reasoning, contextual understanding, and code generation.
However, these advances came at a cost—both financial and computational. Training state-of-the-art models required billions of dollars in investment and massive clusters of high-end GPUs, primarily provided by Nvidia. The assumption was that only well-funded companies with access to large-scale infrastructure could compete at the highest level. Furthermore, US AI policy heavily influenced the global AI landscape, with increasing restrictions on open-source AI development and a focus on proprietary models.
How DeepSeek Changed Everything
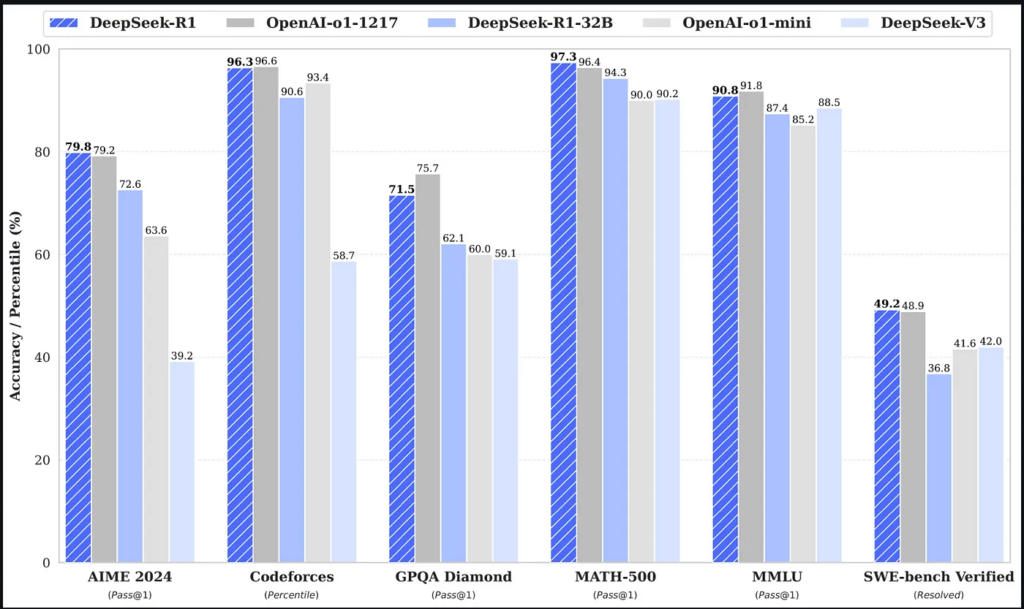
Enter DeepSeek R1, a model that seemingly emerged from nowhere and defied all expectations. Developed in China as a project by a hedge fund looking to generate long-term social value, DeepSeek R1 was released as an open-weight model under the MIT license. Unlike its competitors, DeepSeek R1 was trained at a fraction of the cost—under $10 million—yet managed to outperform OpenAI’s GPT-4-turbo in key reasoning benchmarks.
The most significant differences between DeepSeek R1 and other models are:
- Open-Source Accessibility: Unlike OpenAI’s closed models, DeepSeek R1 is freely available for developers, fostering a new wave of innovation.
- Efficient Training: DeepSeek’s engineers optimized their model to run on consumer hardware, such as Apple M2 Ultras, rather than relying on the latest Nvidia H100 GPUs.
- Cost Disruption: OpenAI charges $60 per million tokens for its premium API, whereas DeepSeek’s costs are as low as $2.19 per million tokens, creating an enormous price gap that is forcing the market to adjust.
- Performance on Reasoning Tasks: Users report that DeepSeek R1 not only excels in traditional benchmarks but also passes the “vibe test” delivering natural and coherent responses in a way that feels intuitive.
How Companies Are Adapting
The rise of DeepSeek R1 has sent shockwaves through Big Tech, forcing companies like Microsoft, Meta, and Amazon to rethink their AI strategies.
- Microsoft: Despite its close partnership with OpenAI, Microsoft swiftly integrated DeepSeek R1 into Azure AI Foundry and GitHub, providing users with more choices. This signals a shift in AI democratization, where companies must support multiple AI ecosystems.
- Meta: As a strong proponent of open-source AI, Meta sees DeepSeek as a validation of its own approach. It is likely to double down on its Llama series while exploring partnerships with other open-weight models.
- Amazon (AWS): AWS quickly adapted by providing detailed guides on how to deploy DeepSeek R1 on Amazon SageMaker and Bedrock. The move highlights how cloud providers recognize the need to support a diverse AI model ecosystem rather than relying solely on proprietary solutions.
Implications for the Future
DeepSeek’s emergence challenges several long-standing assumptions about AI development:
- End of US Dominance? The AI industry has largely been driven by US companies, but DeepSeek demonstrates that China is rapidly closing the gap. If more companies follow DeepSeek’s model, the AI supply chain could shift away from US control. The availability of open-source AI code could accelerate innovation from other countries, leveling the playing field and fostering a more globally competitive AI ecosystem.
- Commoditization of Foundation Models: With open-weight models like DeepSeek R1 offering cutting-edge performance at low costs, selling API access to closed models may become less viable. Instead, value may shift toward application-layer AI services rather than the models themselves.
- Reduced Dependence on Expensive Hardware: DeepSeek’s ability to operate efficiently on consumer-grade hardware suggests a future where high-end GPUs are no longer the primary bottleneck for AI progress. This could have massive implications for companies like Nvidia, which have profited immensely from AI’s reliance on their chips.
- Impact on Nvidia: The rise of efficient, lower-cost AI models like DeepSeek R1 has already caused turbulence in the stock market, with Nvidia experiencing a selloff as investors reconsider the long-term demand for its high-end GPUs. If more AI companies optimize models to run on alternative hardware, Nvidia’s dominance in the AI chip sector could be challenged.
Risks and Challenges of DeepSeek’s Introduction
While DeepSeek R1 presents exciting opportunities, it also comes with several risks and challenges:
- Security Concerns: Open-source AI models can be modified for malicious purposes, making it easier for bad actors to exploit the technology for disinformation, fraud, or cyberattacks.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide may struggle to regulate open-source AI, leading to potential conflicts over AI ethics, data privacy, and content moderation.
- Economic Disruption: The availability of high-performance open-weight models could erode the business models of AI companies that rely on closed systems, potentially leading to job losses and restructuring in the industry.
- Geopolitical Implications: The shift in AI power from the US to China may create new tensions in global technology policy, prompting stricter AI trade restrictions and competition in AI governance frameworks.
In conclusion: Is This AI’s ‘Sputnik Moment’?
DeepSeek R1’s release may very well mark a turning point in the AI industry — a moment comparable to the launch of Sputnik in 1957, which sparked the space race between the US and the Soviet Union. If AI development can be achieved at lower costs, with greater openness, and without reliance on a few centralized tech giants, we may be entering a new era of competition and innovation.
This shift raises crucial questions: Will the US government and Big Tech attempt to curb the rise of open-source AI? Can China maintain its momentum in AI development? And most importantly, what new possibilities will emerge now that powerful AI is becoming accessible to more people worldwide?
One thing is clear—DeepSeek R1 is not just another AI model. It is a symbol of a broader shift that could redefine the AI industry for years to comes.
